Last term during an interim crit, I saw the work my students had produced on the RFID icons brief I set some weeks ago. It was a good afternoon and we were lucky enough to have Timo Arnall from the Touch project and Younghee Jung from Nokia Japan join us and contribute to the discussion. All the students attending showed good work of a high standard, overall it was very rewarding.
I’ll write a more detailed discussion on the results of the work when the brief ends, but I suspect there may be more than I can fit into a single post, so I wanted to point at some of the work that has emerged so far.
All the work here is from Alex Jarvis and Mark Williams.
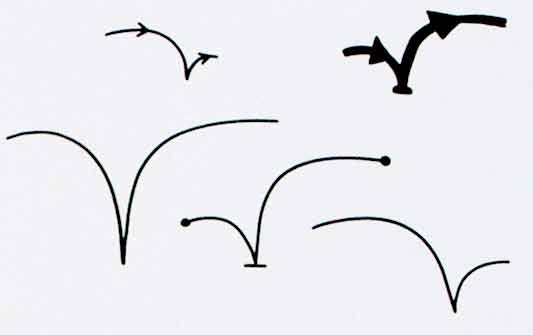
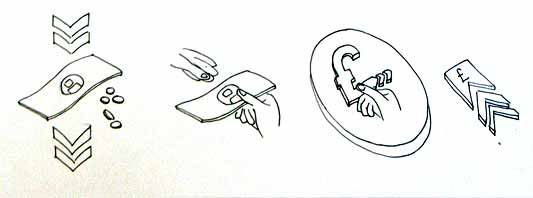
Alex began by looking at the physical act of swiping your phone or card over a reader. The symbol he developed was based on his observations of people slapping their Oyster wallets down as they pass through the gates on to the underground. Not a delicate, patient hover over the yellow disc, but a casual thud, expectant wait for the barrier to open, then a lurching acceleration through to the other side before the gates violently spasm shut.
More developed sketches here…
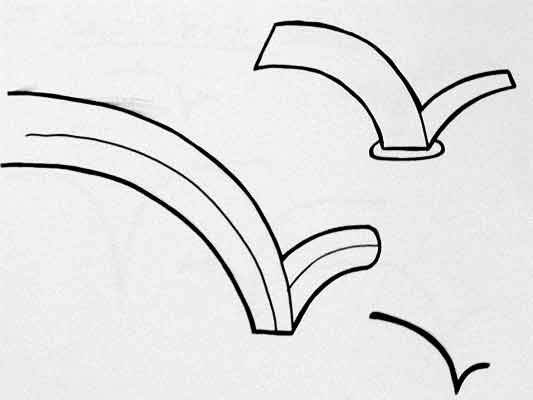
I suspect that this inverted tick will abstract really well, I like the thin line on the more developed version snapping the path of the card into 3D. It succeeds since it doesn’t worry too much about working as an instruction and concentrates more on a powerful cross-system icon to be consistently recognisable.
Verbs
The original brief required students to develop icons for the verbs: purchase, identify, enter (but one way), download, phone and destroy.
Purchase and destroy are the two of these verbs with the most far-reaching and less immediate consequences. The aspiration for this work is to make the interaction feel like a purchase, not a touch that triggers a purchase. This gives the interaction room to grow into the more complex ones that will be needed in the future.
This first sketch, on purchase, from Alex shows your stack of coins depleting, something nice about the dark black arrow which repeats as a feature throughout Alex’s developments.
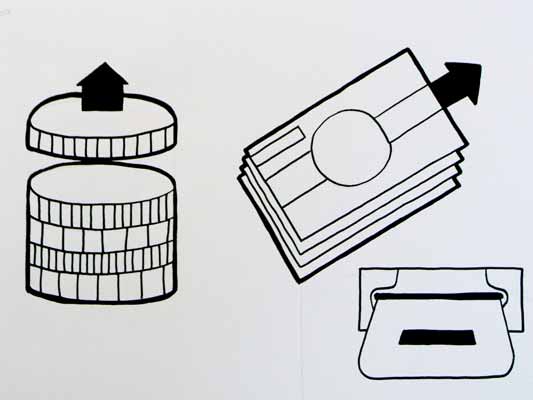
Mark has also been tackling purchase, his sketches tap into the currency symbols, again with a view to represent depletion. Such a blunt representation is attractive, it shouts “this will erode your currency!”
Mark explores some more on purchase here:
Purchase is really important. I can’t think of a system other than Oyster that takes your money so ambiguously. Most purchasing systems require you to enter pin numbers, sign things, swipe cards etc, all really clear unambiguous acts. All you have to do is wave at an Oyster reader and it costs you £2… maybe: The same act will open the barrier for free if you have a travel card on there. Granted, passengers have already made a purchase to put the money on the card, but if Transport for London do want to extend their system for use as a digital wallet they will need to tackle this ambiguity.
Both Mark and Alex produced material looking at the symbols to represent destroy, for instances where swiping the reader would obliterate data on it, or render it useless. This might also serve as a warning for areas where RFID tags were prone to damage.
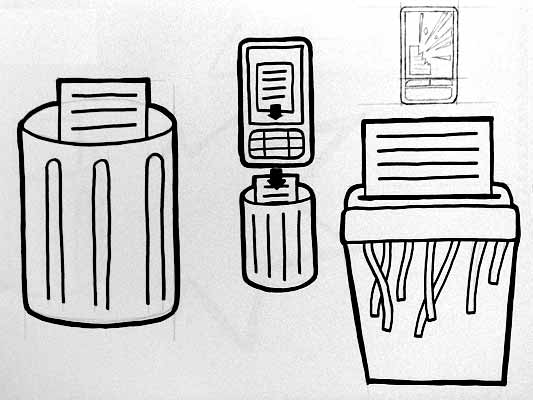
I like the pencil drawing to the top right that he didn’t take forward. I’ve adjusted the contrast over it to draw out some more detail. Important that he distinguished between representing the destruction of the object and the data or contents.
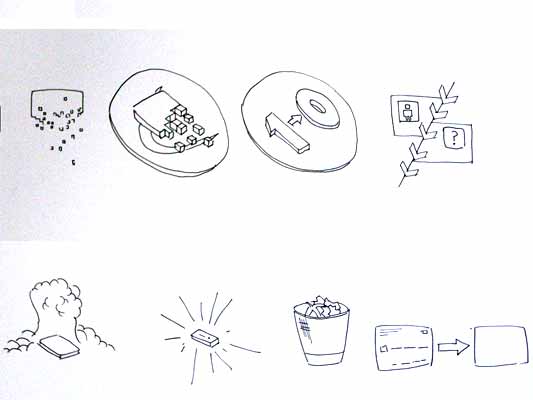
Mark’s sketches for destroy include the excellent mushroom cloud, but he also looks at an abstraction of data disassembly, almost looks like the individual bits of data are floating off into oblivion. Not completely successful since it also reminds me of broadcasting Wonka bars in Charlie and the Chocolate Factory and teleporting in Star Trek, but nice none the less.
Drawing
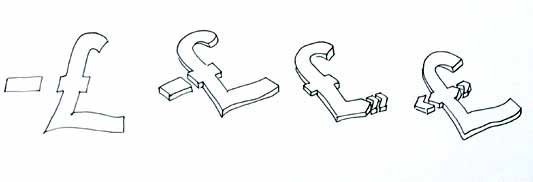
This is difficult to show online, but Alex works with a real pen, at scale. He is seeing the material he’s developing at the same size it will be read at. Each mark he makes he is seeing and responding to as he makes it.
He has produced some material with Illustrator, but it lacked any of the impact his drawings brought to the icons. Drawing with a pen really helps avoid the Adobe poisoning that comes from Illustrator defaults and the complexities of working out of scale with the zoom tool (you can almost smell the 1pt line widths and the 4.2333 mm radius on the corners of the rounded rectangle tool). It forces him to choose every line and width and understand the success and failures that come with those choices. Illustrator does so much for you it barely leaves you with any unique agency at all.
It is interesting to compare the students’ two approaches. Alex works bluntly with bold weighty lines and stubby arrows portraying actual things moving or downloading. Mark tends towards more sophisticated representations and abstractions, and mini comic strips in a single icon. Lightness of touch and branching paths of exploration are his preference.
More to come from both students and I’ll also post some of my own efforts in this area.
